Short Course on Multibody Dynamics
Transcript
Promemoria lezione
AA 2007-2008
Meccanica del Volo
Propulsione
Tipi di propulsione
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Meccanica del Volo
Motore a combustione
interna alternativo
Pratt-Whitney_R-2800
Lycoming O-235C2
Pratt & Whitney R-4360
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Meccanica del Volo
Rolls-Royce
Griffon
Type
12-cylinder supercharged liquid-cooled 60° Vee aircraft piston engine
Power output:
2,035 hp (1,520 kW) at 7,000 ft (2,135 m)
1,820 hp (1,360 kW) at 21,000 ft (6,400 m)
Dry weight:
1,980 lb (900 kg)
Specific power:
0.91 hp/in³ (41.4 kW/L)
Power to weight ratio: 1.03 hp/lb (1.69 kW/kg)
The Rolls-Royce Griffon engine was used in the Schneider Trophy races.
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Meccanica del Volo
Motore stellare a
combustione interna
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Motori stellari o in linea
Meccanica del Volo
The debate about the merits of the radial vs. the inline continued
throughout the 1930s, with both types seeing some use.
The radial was more popular largely due to its simplicityand better
power/weight ratio for aircraft carrier takeoffs.
Although inline engines offer smaller frontal area than radials, inline
engines require the added weight and complexity of cooling systems
and are generally more vulnerable to battle damage.
Originally radial engines had but one row of cylinders, but as engine
sizes increased it became necessary to add extra rows.
Most did not exceed two rows, but the largest radial engine ever built
in quantity, the Pratt & Whitney Wasp Major, was a 28-cylinder 4-row
radial engine used in many large aircraft designs in the post-World
War II period.
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Motore a combustione
interna alternativo
La potenza erogata da
tali motori dipende:
Meccanica del Volo
• dal numero di giri.
La potenza cresce all’aumentare
del numero di giri.
• dalla pressione di alimentazione
manifold pressure funzione della
valvola di regolazione dell’aria air throttle, la farfalla.
• dal rapporto ponderale aria-combustibile
Titolo della miscela: miscela ricca o miscela povera
• dalla quota.
La potenza diminuisce con la quota di volo.
Una formula empirica porta a esprimere la
potenza alla generica quota z come
• è sostanzialmente indipendente dalla velocità di volo
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Meccanica del Volo
P-51 Mustang
If it is well designed, a contra-rotating propeller will have no rotational air flow,
pushing a maximum amount of air uniformly through the propeller disk, resulting in
high performance and low induced energy loss.
It also serves to counter the asymmetrical torque effect of a conventional propeller.
Some contra-rotating systems were designed to be used at take off for maximum
power and efficiency, and allowing one of the propellers to be disabled during cruise
to extend flight time.
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Meccanica del Volo
The first Griffon-powered Spitfire, DP845
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Contra-rotating
propellers
Meccanica del Volo
A Rolls-Royce Griffon powered the North American P-51 Mustang that
was an American long-range single-seat fighter aircraft that entered
service with Allied air forces in the middle years of World War II.
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Jet engines
Meccanica del Volo
Compressore
centrifugo
Compressore
assiale
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Turbofan engines
Low-bypass
Meccanica del Volo
L’uso di turbofan, con piccola
o grande diluizione, riduce i
consumi e contribuisce a
ridurre il livello di rumore
High-bypass
Bypass ratio 2 - 5
Bypass ratio 6 - 9
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Turboshaft
engine
Meccanica del Volo
turboelica
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Carnot's theorem
Meccanica del Volo
Carnot heat engine diagram
Thermal efficiency
is defined as
Carnot’s limit on the
maximum efficiency
The first law of thermodynamics requires
The second law of thermodynamics requires
The third law of thermodynamics requires the use of an absolute temperature scale
Together they imply a maximum heat-to-work efficiency of:
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Carnot's theorem
Thermal efficiency is defined as
Meccanica del Volo
Carnot heat engine diagram
Carnot’s limit on the maximum efficiency
The first law of thermodynamics requires
The second law of thermodynamics requires
The third law of thermodynamics requires the use of an absolute temperature scale.
Together they imply a maximum heat-to-work efficiency of:
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Meccanica del Volo
Evoluzione del consumo specifico
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Meccanica del Volo
Evoluzione dell’inquinamento
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Meccanica del Volo
Turbogetto
All’aumentare della quota la portata in massa diminuisce per effetto
dalla diminuita densità. Sino alla tropopausa, si può esprimere la
trazione T ad una quota assegnata z come
Il consumo specifico cresce all’aumentare della velocità di volo e
rimane circa costante al variare della quota; valore indicativo:
0,8-1,0 N(N h).
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Meccanica del Volo
Gloster E.28/39
The W2/700 engine flew
in the Gloster E.28/39,
the first British aircraft to
fly with a turbojet engine,
and the Gloster Meteor.
In September 1939, the Air Ministry issued a
specification to Gloster for an aircraft to test
one of Frank Whittle's turbojet designs.
Working closely with Whittle, Gloster's chief
designer George Carter laid out a small lowwing aircraft of conventional configuration.
The jet intake was in the nose, and the tail-fin
and elevators were mounted above the jet-pipe.
Le camere di combustione
circonferenziali
A contract for two prototypes was signed by the
Air Ministry on 3 February 1940 and the first of
these was completed by April 1941
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Meccanica del Volo
Me 262
The Messerschmitt Me 262 Schwalbe (German "Swallow") was the world's first
operational jet-powered fighter aircraft. It was produced in World War II and saw
action starting in 1944 in bomber/reconnaissance and fighter/interceptor roles.
Officially named Schwalbe, because the swallow is one of the fastest birds
known when going into a dive to capture and eat an airborne insect, German
pilots nicknamed it the Turbo, while the Allies called it the Stormbird.
While the Me 262 had a negligible impact on the course of the war (approximately
150 Allied aircraft losses for 100 Me 262 losses), its design was highly influential
on postwar aircraft development.
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
DH-106 Comet
Meccanica del Volo
Vickers Viscount
The British de Havilland Comet first flew in
1949 and is noted as the world's first
commercial jet airliner
On 10 January 1954, BOAC Flight 781 a De
Havilland Comet 1 took off from Ciampino
Airport in Rome, Italy en route to Heathrow
Airport in London, England on the final leg
of its flight from Singapore. At about 10:00
GMT, the aircraft suffered an explosive
decompression at altitude and crashed into
the Mediterranean Sea, killing everyone on
board.
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Meccanica del Volo
BOAC Flight 781
After extensive testing of the Comet
1 G-ALYU ("Yoke Uncle") which had
been donated for testing by BOAC,
investigators at the RAE concluded
that the crash had been due to
failure of the pressure cabin at the
forward ADF window in the roof.
This 'window' was in fact one of two apertures for the aerials of an electronic
navigation system, opaque fibreglass panels taking the place of the window
'glass' - as a result of metal fatigue caused by the repeated pressurisation and
de-pressurisation of the aircraft cabin.
In addition, it was discovered that the stresses around pressure cabin apertures
were considerably higher than had been appreciated, especially around sharpcornered cut-outs, such as windows.
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Meccanica del Volo
ugelli
postbruciatore
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Meccanica del Volo
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Trent 900
Leading the way on the Airbus A380
Engine Specification
Meccanica del Volo
SL 0.25M,
flat-rated to 30°C/86°F
Thrust
70,000-76,500lb
Certificated up to 80,000lb
Bypass ratio
Inlet mass flow
8.7-8.5
2655-2745lb/sec
Fan diameter
116in
Length
179in
Weight
14,190lb
Stages
Fan, 8 IPC, 6 HPC
1 HPT, 1 IPT, 5 LPT
Certification 29th October 2004
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
GE90-115B
Meccanica del Volo
Fan/Compressor Stages: 1F/4LPC/9HPC
Low-Pressure Turbine/High-Pressure Turbine Stages: 6/2
Application Examples:
Boeing 777-200LR
Boeing 777-300ER
Max Diameter (Inches): 135
Length (Inches): 287
Dry Weight (Lb.): 18,260
Max. Power at Sea Level (Lb.): 115,300
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Meccanica del Volo
GE90-115B
E’ il motore più grande e più
potente al mondo.
Certificato per 115000 lb
52.000 kg, ha sviluppato in
prova una spinta di 127900 lb,
58000 kg.
Il diametro misura poco meno
di tre metri e mezzo. Visto da
vicino lascia particolarmente
stupiti,
fa
decisamente
impressione.
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Statoreattore
scramjet
Meccanica del Volo
supersonic combustion ramjet
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Boeing X-43
Meccanica del Volo
Guinness
World
Records
recognized
NASA's
X-43A
scramjet with a new world speed
record for a jet-powered aircraft
Mach 9.6, or nearly 7,000 mph.
Pegasus booster rocket ignites to send
the X-43A on its record setting flight on
Nov. 16, 2004. NASA photo
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Aerospaziale
Politecnico di Milano
Documenti analoghi
Meccanica del Volo Promemoria lezione
 Five flights were made
HyShot I was launched on 30 October 2001
HyShot II was launched on 30 July 2002
HyShot III was launched on 25 March 2006
HyShot IV was launched on 30 March 2006
HyCAUSE was l...
Five flights were made
HyShot I was launched on 30 October 2001
HyShot II was launched on 30 July 2002
HyShot III was launched on 25 March 2006
HyShot IV was launched on 30 March 2006
HyCAUSE was l...
Meccanica del Volo Promemoria lezione
 Maximum speed: 570 mph, (920 km/h)
Range: 3,257 nm (3,749 mi, 6,033 km)
Service ceiling: 34,000 ft (10.4 km)
Rate of climb: 1,800 ft/min (9.1 m/s)
Maximum speed: 570 mph, (920 km/h)
Range: 3,257 nm (3,749 mi, 6,033 km)
Service ceiling: 34,000 ft (10.4 km)
Rate of climb: 1,800 ft/min (9.1 m/s)
Potenze e rendimenti - Politecnico di Milano
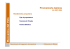 L’uso di turbofan, con piccola
o grande diluizione, riduce I
consumi e contribuisce a
ridurre il livello di rumore
L’uso di turbofan, con piccola
o grande diluizione, riduce I
consumi e contribuisce a
ridurre il livello di rumore
Equazioni di equilibrio al beccheggio
 The Northrop YB-49 was a prototype jet-powered flying wing
medium bomber aircraft developed by Northrop for the United
YB49
States Air Force shortly after World War II. It was a development of
the ...
The Northrop YB-49 was a prototype jet-powered flying wing
medium bomber aircraft developed by Northrop for the United
YB49
States Air Force shortly after World War II. It was a development of
the ...