Vaccination against Papilloma virus
Transcript
Vaccination against Papilloma virus
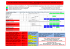
WHAT IS THE CERVIX? It is the lower part of the uterus, which opens into the vagina. IS CERVICAL CANCER WIDESPREAD? In Italy, 3,400 new cases of cervical cancer are diagnosed on an annual basis. They lead to 1,000 deaths every year. WHAT IS THE MAIN CAUSE OF CERVICAL CANCER? Cervical cancer is due to some types of viruses, for example, the Human Papilloma Virus (HPV). Vaccination against Papilloma virus: why and how VACCINATION Vaccination against some types of Human Papilloma Virus has been available since 2007. The vaccine is safe and effective. Vaccination is performed at the ambulatori vaccinali (vaccination centres) in the ASL (Local Healthcare Units). It is free for girls aged more than 11, but also women up to 45 years of age can be vaccinated (with a quadrivalent vaccine) upon payment of the "ticket" (healthcare service fee). TO KNOW MORE... READ INSIDE By the Cancer Screening UOC (Complex Operational Unit) Via Monza 2, Roma 00154 tel. 0651006600 e.mail: [email protected] Last updated: November 2014 an opportunity to prevent cervical cancer WHAT IS PAPILLOMA VIRUS (HPV)? Papilloma is extremely widespread: there are several types of viruses and more than 40 of them may lead to infections of the female genital apparatus. 13 of these viruses are considered "high risk", because they may cause cell alterations and, rarely, develop into cancerous lesions. Generally, these infections are transitory, symptomless, and 90% of them heals spontaneously. HOW IS PAPILLOMA VIRUS TRANSMITTED? The most common means of transmission is by sexual intercourse. Using a condom helps significantly reduce virus transmission; however, it does not guarantee total protection since the virus can be on an area of skin not covered by the condom. WHAT MAY PAPILLOMA VIRUS CAUSE IN A WOMAN? HPV is the most common sexually transmitted disease, especially before 25 years of age. Some types of HPV, especially type 16 and type 18, may, in some rare cases, cause cervical cell alteration. Such alteration, if persistent and left untreated, may slowly develop into cancer. It is necessary to remember that over 70% of cases of cervical cancer is due to a persistent HPV 16 and 18 infection. A cancer may develop several years - even twenty years - after actual infection. Besides persistent HPV 16 and 18 infection, other factors that may contribute to cancer development are: cigarette smoke, prolonged use of oral contraceptives, and HIV infection. If a woman gets pregnant after having started the vaccination cycle, she must wait for her pregnancy to be finished in order to complete vaccination. IF I AM VACCINATED, SHOULD I HAVE A PAP TEST? The vaccine only protects women from Type 16 and 18 Papilloma virus, the viruses that most frequently cause cervical cancer. The Pap test allows to detect cervical cell alterations, also those caused by types of HPV not covered by vaccine. Therefore, every woman should have a Pap Test, vaccinated or not. Today, the combination of vaccination and Pap test is the most effective and complete way to prevent cervical cancer. Vaccination does not replace Pap test screening and screening does not replace vaccination: a combination of the two is recommended. The ASL Roma C has implemented a Screening programme for prevention and early diagnosis of cervical cancer. The programme includes a reminder letter sent to women aged between 25 and 64 to remind them to have a Pap test every three years, as recommended by national and international guidelines. Interested women - also those who have not received a letter may register for Pap Test by calling the screening programme Numero Verde (free toll number) 800405051 every day, from Monday to Friday, 08:00 a.m.-18:00 p.m. FOR FURTHER INFORMATION You may address the Vaccination Centres of the ASL where you reside, Consultori famigliari, your Paediatrician and your Medico di Famiglia (General Practitioner). Please make reference to the following websites: www.salute.gov.it> Temi > Prevenzione > Malattie infettive e vaccinazioni > Domande più frequenti > FAQ - Vaccinazione contro il papilloma virus by the Ministero della salute (Ministry of Healthcare) www.epicentro.iss.it> malattie infettive > infezioni da hpv by the Istituto Superiore di Sanità (National Healthcare Institute) www.vaccinarSì.org by the Società Italiana di Igiene Medicina preventiva e Sanità pubblica (Italian Society for Preventive Medical Hygiene and Public Healthcare) http://www.gisci.it/documenti/documenti_gisci/100d_hpv_2013.pdf by the Osservatorio nazionale degli screening (National Screening Observatory) IS THE VACCINE SAFE? Yes, because the vaccine does not contain live attenuated virus, but it is made of virus-like synthetic particles. This means that there is no risk of infection due to the vaccine. Severe adverse reactions to administration of the vaccine are extremely rare. More frequently, the vaccine may cause some pain: collateral effects such as temperature, nausea, dizziness, headache and joint pain may arise sometimes. However, such symptoms are generally mild and they last only a short period of time. IS THE VACCINE EFFECTIVE? Clinical studies have shown that the vaccine, if administered when the woman has not got in touch with the virus yet, ensures a very high degree (90-100%) of protection from HPV 16 and 18 infections and from the precancerous lesions they cause. However, approximately 30% of cervical cancers are not caused by HPV 16 and 18. Therefore, it is important to continue having a routine Pap test even after having been vaccinated. HOW LONG AM I PROTECTED FROM THE VIRUS? Currently available studies have shown that protection lasts at least 9 years after vaccination. In the future, further studies will provide information on a potentially longer protection period and on the need of vaccine boosters. WHO SHOULD GET VACCINATED? The vaccine's goal is to prevent infection, not to cure it; therefore, it is necessary to administer the vaccine before any potential contact with the virus, that is, before sex debut (first sexual intercourse). If a girl has already been exposed to the virus, the effectiveness of vaccination in preventing infections and precancerous lesions caused by HPV 16 and 18 sharply decreases to approximately 40%. WHO CAN BE VACCINATED FOR FREE? The SSN (National Healthcare Service) provides for free vaccination to all girls during their 12th year of life (when they turn 11). The ASL of the area of residence invites all interested girls to be vaccinated by sending a reminder letter at home. WHAT DOES THE SSN (National Healthcare Service) PROVIDE FOR WOMEN AGED MORE THAN 12? Currently, all girls who have not been vaccinated during their 12 th year of age may get vaccinated for free before they turn 19 at the Servizi vaccinali (Vaccination Service Unit) in their ASL of reference. Clinical studies have shown that vaccination is effective and safe also for women up to 45 (quadrivalent vaccine) or 55 years of age (bivalent vaccine). It must be pointed out that the effectiveness of the vaccine decreases significantly after the woman starts having sexual intercourse. Therefore, the SSN does not systematically offer vaccination to women in this age range. These women may, however, get vaccinated at a reduced price at the Servizi vaccinali of their ASL of reference (see table below): WHO ADMINISTERS THE VACCINE AND WHERE AND WHEN CAN I GET VACCINATED? Vaccination is carried out by healthcare professionals in the vaccine centres in the ASL (see table below). The vaccine is administered via 2 intramuscular injections in the upper part of the arm (deltoid muscle) over a period of 6 months (3 doses for girls aged more than 14). CAN BOYS AND MEN GET VACCINATED? Currently, some Italian regions offer vaccination also to boys and men. However, Lazio is not among these regions. The vaccine has been found to be effective also in preventing cancerous lesions on the penis, anal, and perianal area caused by Papilloma virus. This would help decrease the risk of virus transmission during sex. CENTRI VACCINALI ASL ROMA C (AGE RANGE FOR VACCINATION, ADDRESS AND TELEPHONE NUMBER) Distretto VI Distretto IX Distretto XI 11-45 Servizio di Medicina preventiva dell’età evolutiva (Childhood and Adolescence Preventive Medicine Centre) Via Telese, 80 (0651003037) 18-45 Servizio di Igiene e Sanità Pubblica (Public Hygiene and Healthcare Centre) Via N. Forteguerri, 4 (0651005230) 11-45 Consultori Familiari Via Casilina, 711 (0651008900/8901) Via H. Spencer, 282 (0651008804) Piazza dei Condottieri, 34 (0651008553) 11-18 Servizio di Medicina preventiva dell’età evolutiva (Childhood and Adolescence Preventive Medicine Centre) Via Nocera Umbra, 110 (0651008713) 18-45 Consultori Familiari Via Monza, 2 (0651006518) Via C. Denina, 7 (0651008571/8574) Via Iberia, 73 (0651008580/8581) 11-45 Servizio di Medicina preventiva dell’età evolutiva (Childhood and Adolescence Preventive Medicine Centre) Via S. Nemesio, 28 (0651003781/5) 18-45 Servizio di Igiene e Sanità Pubblica (Public Hygiene and Healthcare Centre) 13-45 anni Consultorio Familiare Largo Sette Chiese, 25 (0651008836/8896) Via del Casale De Merode, 8 (0651003768) Distretto XII 11-45 Servizio di Medicina preventiva dell’età evolutiva (Childhood and Adolescence Preventive Medicine Centre) Via I. Silone, 100 (0651008295/8296) Centro della Gioia Via Ardeatina, 1227 (0651008636) Via Noventa, 1 (0651008666) Via Frignani, 83 (0651008684) Via Sabatini, s.n.c.(0651006447) 18-45 Servizio di Igiene e Sanità Pubblica (Public Hygiene and Healthcare Centre) Centro della Gioia Via Ardeatina, 1227 (0651008641) 13-45 anni Consultorio Familiare Via N. Stame, 162 (0651008276) CAN I GET VACCINATED DURING PREGNANCY? Pregnant women cannot get vaccinated, because available clinical studies have not yet produced final results on the safety of vaccination during pregnancy. DOES HPV INFECTION REGARD ONLY WOMEN? No, also men can be infected. However, HPV only very rarely develops cancerous alterations on male genitalia. HOW IS HPV TREATED? The virus cannot be eliminated. Therefore, early diagnosis of cervical alterations caused by HPV is of vital importance. Such early diagnosis is possible thanks to Pap test. In this way, it will be possible to detect any potentially dangerous cervical lesions, that may be subsequently monitored or treated. CAN HPV INFECTION BE PREVENTED? Yes. There are currently 2 types of HPV vaccines available on the market: Cervarix and Gardasil. Cervarix only protects from 16 and 18- type HPV; Gardasil, which is widely used in the Regione Lazio healthcare centres, protects also from 6 and 11- type HPV. These types of HPV potentially cause genital condyloma. WHAT IS GENITAL CONDYLOMA? Condyloma consists of small, benign, pink growths. They can be smooth or slightly bumpy to the touch, single or clustered. They mainly occur on external genitals or in the perianal region. Condyloma are painless and they only occasionally cause itching. Also condyloma is caused by sexually transmitted HPV infection. Condyloma can be effectively treated and does not develop into cancer. Using a condom does not ensure complete protection, since areas at risk of infection can be on an area of skin not covered by the condom.
Documenti analoghi
RUBELLA WHY RUN THE RISK?
 A blood test is needed to be sure that a person bone alterations
has had the illness before.
A blood test is needed to be sure that a person bone alterations
has had the illness before.